[svelte store][03] StopWatch 구현하기
이번 글에서는 svelte store의 get(), readable(), writable()을 이용해서 stop watch 를 구현합니다.
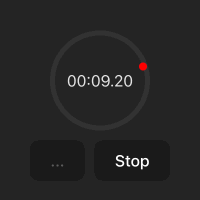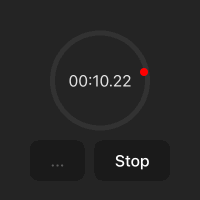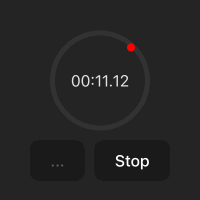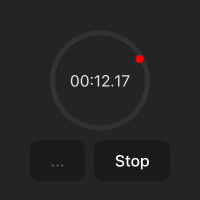
화면 구성
스탑워치 화면은 다음과 같습니다.
StopWatch.svelte<script lang="ts">
</script>
<section class="flex-center">
<div class="time-display flex-center">
<span class="point"></span>
<span>00:00:00</span>
</div>
<div class="buttons">
<button>Start</button>
<button>Stop</button>
</div>
</section>
<style lang="scss">
.flex-center {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
section {
flex-direction: column;
gap: 10px;
.time-display {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 5px solid #333;
border-radius: 50%;
position: relative;
box-sizing: border-box;
.point {
position: absolute;
width: 8px;
height: 8px;
background-color: red;
border-radius: 50%;
top: 0%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
}
.buttons {
display: flex;
gap: 10px;
}
}
</style>
.time-display는 스탑워치의 원에 해당합니다..point는 원의 둘레를 1초마다 회전하는 빨간색 점입나다. 현재 원의 위쪽에 위치해 있습니다(top: 0%; left: 50%;).- start/stop - 스탑워치를 시작하고 중지시킵니다.
StopWatch.svelte는 아무런 기능이 없습니다.
이제 스탑워치의 상태를 관리하는 svelte store 구현체를 만들어서 화면에 적용할 것입니다.
stopwatch.store.ts
스탑워치의 상태를 관리하는 svelte store 구현체는 다음과 같은 인터페이스를 제공합니다.
TYPESCRIPTexport type Millis = number;
export type StopWatchState = {
running: boolean;
elapsed: Millis;
px: number;
py: number;
};
export const createStopWatch = () => {
let startTime: number = 0;
let timer: number = 0;
const store = writable({
running: false,
elapsed: 0,
px: 50,
py: 0
});
/** format elapsed as "mm:ss.SS"
*/
function formatTime(state:StopWatchState):string {
return "00:00:00";
}
/** start stopwatch
*/
function start():void {}
/** stop stopwatch
*/
function stop():void {}
return {
store,
stopWatch: {
start,
stop,
formatTime
}
};
}
starTime - 스탑워치를 시작한 시간을 저장합니다.
running, elapsed, (px, py) - 스탑워치의 상태에 해당합니다. (px, py)는 빨간 점을 원 위에 나타내기 위한 좌표값입니다.
함수 start()와 stop()으로 스탑워치의 상태를 변경하고 View에서 변경을 감지할 수 있도록 svelte store 객체를(const store) 함께 반환합니다. 함수 formatTime()은 경과 시간을 "mm:ss.SS" 문자열로 반환합니다.
가독성을 위해서 함수들을 stopWatch 로 감싸서 반환합니다.
StopWatch.svelte에서는 다음과 같이 store 객체를 사용합니다.
StopWatch.svelte<script lang="ts">
import { createStopWatch } from './stopwatch.store';
const { store, stopWatch } = createStopWatch();
</script>
<section class="flex-center">
<div class="time-display flex-center">
<span class="point"></span>
<span>{stopWatch.formatTime($store)}</span>
</div>
<div class="buttons">
<button on:click={() => stopWatch.start()}>Start</button>
<button on:click={() => stopWatch.stop()}>Stop</button>
</div>
</section>
store- 상태를 조회하기 위한 svelte store 객체stopWatch- 상태를 변경할 함수들을 제공함(start, stop, formatText).
{stopWatch.formatTime($store)} - View에서 text를 삽입할 때 {...} 문법을 사용합니다. vue의 {{..}}에 해당합니다. 변수 store는 svelte store 객체이므로 reactive하게 경과 시간을 업데이트하기 위해서 store prefix를 붙여서($store) 함수의 인자로 전달합니다.
stopWatch.formatTime()
formatTime 함수를 구현합니다.
stopwatch.store.tsexport const createStopWatch = () => {
const store = wrtiable(...)
/**
* format elapsed as "mm:ss.SS"
*/
function formatTime(state:StopWatchState):string {
const {elapsed} = state;
const seconds = Math.floor(elapsed / 1000);
const mm = pad2(seconds / 60)
const ss = pad2(seconds % 60);
const SS = pad2((elapsed % 1000) / 10)
return `${mm}:${ss}.${SS}`;
}
}
stopwatch.store.ts에서 변수 store 의 타입은 Writable<StopWatchState> 입니다.
stopwatch.store.tsimport { ..., writable, type Writable } from 'svelte/store';
export const createStopWatch = () => {
const store:Writable<StopWatchState> = ...;
function formatTime(state:StopWatchState):string { ... }
}
StopWatch.svelte 에서 store prefix를 붙여서 stopWatch.formatTime($store) 와 같이 호출하면 $store의 타입은 StopWatchState 입니다.
stopWatch.start()
Start 버튼을 클릭해서 스탑워치를 실행합니다. 함수 start()를 다음과 같이 구현합니다.
start(), stopwatch.store.tsimport { get, ... } from 'svelte/store';
export const createStopWatch = () => {
function start() {
if (get(store).running) {
return;
}
startTime = Date.now();
store.update((state) => {
state.running = true;
updatePosition(state);
return state;
});
timer = setInterval(updateTime, 10);
}
}
get(store).running - svelte store 객체가 감싸고 있는 상태 StopWatchState 에 접속하려면 함수 get()을 사용합니다. svelte 컴포넌트에서는 $store.running 으로 상태 정보를 접속할 수 있지만 일반 ts(js) 파일에서는 함수 get()을 이용해야 합니다.
store.update((state) => ...) - elapsed와 running 변수를 설정해서 스탑워치를 시작합니다. get()으로 읽어들인 후 store.set()으로 변경된 상태를 저장할 수도 있고 update(...)를 호출해서 상태를 변경할 수 있습니다.
updatePosition() - 스탑워치의 경과 시간과 빨간 점의 위치를 업데이트하는 함수입니다.
setInterval(updateTime, 10); - 10밀리세컨드마다 스탑워치 상태를 변경하는 함수 updateTime을 호출합니다.
store.update(callback)
writable()을 호출해서 반환받은 svelte store 객체에 대해 update()를 사용할 때는 주의할 점이 있습니다.
Use of store.update()store.update((state) => {
// 1. modifications here
...
// 2. Do return state;
return state;
});
doSomeTaksk();
- callback을 등록하면 상태 정보를 인자로 전달받습니다.
- 반드시 전달받은 상태를 다시 반환해야 합니다.
- Typescript에서는 컴파일 오류를 보여주지만 Javascript에서는 문법 오류를 보여주지 않기 때문에 주의해야 합니다.
- 상태를 변경하는 callback 함수는 동기적으로 호출됩니다. 즉, callback이 완전히 실행된 후에
doSomeTask()를 실행합니다.
store.set()또는store.update()를 호출하면 svelte store 객체를 참조하는 view는 reactive 하게 업데이트됩니다.
updatePosition(), updateTime()
이 함수들은 private function 입니다. start()나 stop()과 달리 인터페이스에 노출되지 않습니다.
TS function updatePosition(state: StopWatchState) {
const angle = (state.elapsed / 1000) * 2 * Math.PI;
const radius = 50;
state.px = 50 + radius * Math.sin(angle);
state.py = 50 - radius * Math.cos(angle);
}
function updateTime() {
if (get(store).running) {
store.update((state) => {
state.elapsed = Date.now() - startTime;
updatePosition(state);
return state;
});
}
}
updatePosition() - 1000밀리세컨드를 원의 360도에 맵핑합니다. 이 값은 StopWatch.svelte에서 css variable로 전달됩니다.
(px, py) to css variables
함수 updatePositon()에서 빨간 점의 위치를 업데이트합니다.
(px, py)를 다음과 같이 컴포넌트에 반영합니다.
StopWatch.svelte(View)<section class="flex-center"
style="--point-x: {$store.px}%; --point-y: {$store.py}%">
</section>
$store.px,$store.py- reactive하게 변경된 값을 읽어들여서 자동으로 css variable 값을 업데이트합니다.
css에서는 다음과 같이 top, left property 를 수정합니다.
StopWatch.svelte(SCSS)<style lang="scss">
section {
...
.time-display {
...
.point {
...
top: var(--point-y);
left: var(--point-x);
...
}
}
}
</style>
running state
스탑워치가 실행 중일 때는 START 버튼을 비활성화합니다.
StopWatch.svelte(Html)<section class="flex-center"
style="--point-x: {$store.px}%; --point-y: {$store.py}%">
<div class="buttons">
<button on:click={() => stopWatch.start()}
disabled={$store.running}>{$store.running ? '...' : 'Start'}</button>
<button>Stop</button>
</div>
</section>
disabled={$store.running} - 스탑워치가 실행 중이면 버튼은 disable 됩니다.
{$store.running ? '...' : 'Start'} - 스탑워치가 실행중이면 버튼의 텍스트를 변경합니다.
최종 코드
StopWatch.svelte<script lang="ts">
import { createStopWatch } from './stopwatch.store';
const { store, stopWatch } = createStopWatch();
</script>
<section
class="flex-center"
style="--point-x: {$store.px}%; --point-y: {$store.py}%">
<div class="time-display flex-center">
<span class="point"></span>
<span>{stopWatch.formatTime($store)}</span>
</div>
<div class="buttons">
<button on:click={() => stopWatch.start()}
disabled={$store.running}>{$store.running ?
'...' : 'Start'}</button>
<button on:click={() => stopWatch.stop()}>Stop</button>
</div>
</section>
<style lang="scss">
.flex-center {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
section {
flex-direction: column;
gap: 10px;
.time-display {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 5px solid #333;
border-radius: 50%;
position: relative;
box-sizing: border-box;
.point {
position: absolute;
width: 8px;
height: 8px;
background-color: red;
border-radius: 50%;
top: var(--point-y);
left: var(--point-x);
transform-origin: center;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
}
.buttons {
display: flex;
gap: 10px;
}
}
</style>
stopwatch.store.tsimport { get,
readable,
writable,
type Writable } from 'svelte/store';
export type Millis = number;
export type StopWatchState = {
running: boolean;
elapsed: Millis;
px: number;
py: number;
};
export const createStopWatch = () => {
let startTime: number = 0;
let timer: number = 0;
const store:Writable<StopWatchState> = writable({
running: false,
elapsed: 0,
px: 50,
py: 0
});
function pad2(int:number) {
return Math.floor(int).toString().padStart(2, '0');
}
function formatTime(state:StopWatchState) {
const {elapsed} = state;
const seconds = Math.floor(elapsed / 1000);
const mm = pad2(seconds / 60)
const ss = pad2(seconds % 60);
const SS = pad2((elapsed % 1000) / 10)
return `${mm}:${ss}.${SS}`;
}
function updatePosition(state: StopWatchState) {
const angle = (state.elapsed / 1000) * 2 * Math.PI;
const radius = 50;
state.px = 50 + radius * Math.sin(angle);
state.py = 50 - radius * Math.cos(angle);
}
function updateTime() {
if (get(store).running) {
store.update((state) => {
state.elapsed = Date.now() - startTime;
updatePosition(state);
return state;
});
}
}
function start() {
if (get(store).running) {
return;
}
startTime = Date.now();
store.update((state) => {
state.running = true;
updatePosition(state);
return state;
});
timer = setInterval(updateTime, 10);
}
function stop() {
clearInterval(timer);
store.update((state) => {
state.running = false;
state.elapsed = 0;
updatePosition(state);
return state;
});
}
return {
store,
stopWatch: {
start,
stop,
formatTime
}
};
};
readable()
stopwatch.store.ts에서 읽기와 쓰기가 모두 가능한 store 객체를 view에 노출시키고 있습니다.
stopwatch.store.ts const store:Writable<StopWatchState> = writable({
running: false,
elapsed: 0,
px: 50,
py: 0
});
return {
store,
...
};
View에서는 다음과 같이 직접 store 객체를 업데이트할 수도 있습니다.
AnotherComponent.svelte<script lang="ts">
import { createStopWatch } from './stopwatch.store';
const { store, stopWatch } = createStopWatch();
function resetStopWatch = () => {
$store = { running: false, ...} // store.set(...)
}
</script>
store 객체를 읽기 전용으로 노출시키면 위와 같은 잘못된 연산을 차단할 수 있습니다.
exposing readable storeimport { get, readable, writable, ... } from 'svelte/store';
export const createStopWatch = () => {
const store = writable({...});
const readableStore = readable(get(store), (set) => {
const unsub = store.subscribe((state) => {
set(state);
});
return unsub;
})
return {
store: readableStore,
...
};
}
readable함수는 첫번째 인자로 초기값을 받습니다.
두번째 인자는 readable store의 내부 상태를 변경할 수 있는 callback을 등록합니다.
callback을 통해서 함수(set())을 전달받고, set(..)을 호출하면 readable store의 상태를 변경할 수 있습니다.
readableStore는 stop watch의 변경된 상태를 실시간으로 반영해야 하므로 store.subscribe를 통해서 상태 변화를 관찰합니다.
store.subscribe(..) const unsub = store.subscribe((state) => {
set(state);
});
return unsub;
이제 AnotherComponent.svelte에서 set을 호출하는 아래의 코드는 오류를 발생시킵니다.
AnotherComponent.svelte $store = { running: false, ...} // not executed
- writable store와 달리 readable store는 메소드
set(..)이 없습니다. - readable store의 상태 변경은 오로지 store 내부의 callback에서만 가능합니다.